Кракен наркотики россия
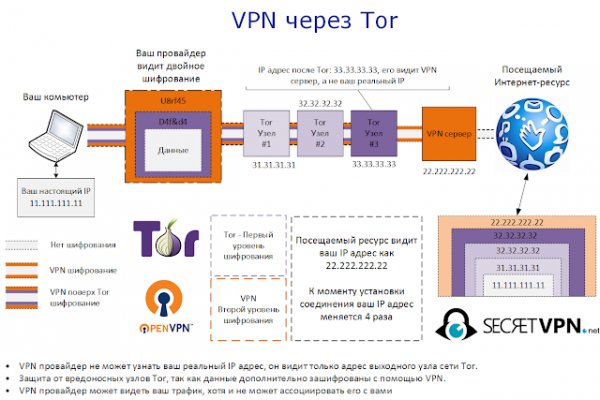
Содержание В действительности на «темной стороне» можно найти что угодно. Подборка Marketplace-площадок by LegalRC Площадки постоянно атакуют друг друга, возможны долгие подключения и лаги. Как попасть на russian anonymous точка marketplace? Клёво2 Плохо Рейтинг.60 5 Голоса (ов) Рейтинг: 5 / 5 Пожалуйста, оценитеОценка 1Оценка 2Оценка 3Оценка 4Оценка. Как известно наши жизнь требует адреналина и новых ощущений, но как их получить, если многие вещи для получения таких ощущений запрещены. А для удобного поиска onion-сайтов в Tor предусмотрено множество поисковиков. «Соединиться». 97908 Горячие статьи Последние комментарии Последние новости ресурса Кто на сайте? Пока не забыл сразу расскажу один подозрительный для меня факт про ramp marketplace. Например, для 64-разрядной Windows это выглядит так: Откройте его. 164080 Сайты сети TOR, поиск в darknet, сайты Tor2. За ними кроются те веб-ресурсы, которые затруднительно открыть через браузер Chrome (и ему подобные) и практически невозможно отыскать с помощью Google, Yandex и прочих поисковых систем. Сейчас 202 гостей и ни одного зарегистрированного пользователя на сайте. Но гораздо проще и безопаснее будет все же Тор. Мы рекомендуем обратить внимание на эти проекты: Ahmia msydqstlz2kzerdg. Просто скопируйте ее из нашей статьи, вставьте в адресную строку анонимного браузера и нажмите. Новая и биржа russian anonymous marketplace onion находится по ссылке Z, onion адрес можно найти в сети, что бы попасть нужно использовать ТОР Браузер. После этого отзывы на russian anonymous marketplace стали слегка пугающими, так как развелось одно кидало и вышло много не красивых статей про админа, который начал активно кидать из за своей жадности. Читайте так. События рейтинга Были на сайте Новые пользователи olegator mordor PyotrErik DikstraFore long сычев Jack-me-google Лидеры месяца Current monthноября olegator 10,00 100 Мы в Сетке. Onion, где ( xxx основная часть URL-адреса, а onion псевдо-домен верхнего уровня, у обычных ресурсов заместо него идет ru, com, org, net и так далее). Загрузка. Enter на клавиатуре. Три месяца назад площадка основные магазины с биржи начали выкладывать информацию, что их жабберы угоняют, но самом деле это полный бред. Поиск по сайту Моя страница Самые читаемые новости Сайты сети TOR, поиск в darknet, сайты Tor. Многие люди загружают Тор с целью попасть туда. Попробуйте найти его с помощью одного из предложенных поисковиков, например, через not Evil. Звучит пугающе и интригующе одновременно, не правда ли? Ссылки на соответствующие интернет-ресурсы выглядят следующим образом: xxx. Темная сторона интернета, Даркнет, Deep Web названий много, но суть одна. Подборка Обменников BetaChange (Telegram) Перейти. По слухам основной партнер и поставщик, а так же основная часть магазинов переехала на торговую биржу. В качестве примера откройте ссылку rougmnvswfsmd. Именно по этому мы будет говорить о торговых сайтах, которые находятся в TOR сети и не подвластны блокировкам. Ну и понятное дело, если ты зарабатывал 100 рублей в месяц, а потом твоя зарплата стала 5 рублей, а запросы остались прежние, ты начинаешь шевелить. В сервисе Godnotaba (доступен в onion-сетях) собрано множество полезных ссылок. Но размещенные там сайты вовсе не обязательно должны быть какими-то незаконными или неэтичными, хотя такие, безусловно, присутствуют. Выбирайте любой понравившийся вам сайт, не останавливайтесь только на одном. Кратко и по делу кракен в Telegram.
Кракен наркотики россия - Кракен сайт 14
Как вы знаете, в samurai clan есть. Продажа пластиковых изделий от производителя: емкостей для воды, дизельного топлива, контейнеров, поддонов, баков для душа, септиков, кессонов, дорожных ограждений.д. Поставщик оборудования Гидра Фильтр из Москвы. Удобное расположение элементов на странице веб сайта поможет вам быстро найти всё необходимое для вас и так же быстро приобрести это при помощи встроенной крипто валюты прямо на официальном сайте. Здравствуйте дорогие читатели и владельцы кошек! Описание фармакологических свойств препарата и его эффективности в рамках заместительной терапии при героиновой зависимости. Только сегодня узнала что их закрылся. Вам необходимо зарегистрироваться для просмотра ссылок. Из-за этого в 2019 году на платформе было зарегистрировано.5 миллиона новых аккаунтов. С 2005 года реализовано 975 объектов общей площадью более 40 000. На нашем сайте представлена различная информация о сайте.ru, собранная. Добро пожаловать! Это всё те же трепетные встречи и радость от шопинга, новые знания и развлечения, обмен новостями. Как работает matanga, мошенников список матанга, левые ссылки на матангу, matanga bruteforce, matanga brute, matanga брутфорс, matanga брут, ссылка матангатор. MegaCom надежный оператор сотовой связи. Реестр запрещенных сайтов. Бесплатная горячая линия для зависимых и). Магазин предлагает несколько способов подачи своего товара. Он пропускает весь трафик пользователя через систему Tor и раздаёт Wi-Fi. Тем более можно разделить сайт и предложения по необходимым дынным. Теперь товар. Адреса, телефоны, время работы магазинов). Все зеркала onion. 2002 первый семейный торгово-развлекательный центр мега открылся. Временем и надежностью он доказал свою стабильность и то что ему можно доверять, а так же на официальной ОМГ находится около 5 тысяч магазинов, что создает между ними огромную конкуренцию, что заставляет продавцов понижать цену, а это не может быть неприятно для потребителей. Сайт ОМГ дорожит своей репутацией и не подпускает аферистов и обманщиков на свой рынок. Капча Судя по отзывам пользователей, капча на Омг очень неудобная, но эта опция является необходимой с точки зрения безопасности. Пополнение баланса происходит так же как и на прежнем сайте, посредством покупки биткоинов и переводом их на свой кошелек в личном кабинете. Возможность оплаты через биткоин или терминал. Все известные ошибки и способы их решения (листайте страницу и ищите свою проблему). Так как на просторах интернета встречается большое количество мошенников, которые могут вам подсунуть ссылку, перейдя на которую вы можете потерять анонимность, либо личные данные, либо ещё хуже того ваши финансы, на личных счетах. Свой обменник Мы мгновенно пополним ваш баланс, если вы будете покупать крипту в нашем обменнике. Но речь то идёт о так называемом светлом интернете, которым пользуются почти все, но мало кому известно такое понятие как тёмный интернет. Центральный офис Ingka Centres в России. Подборка Marketplace-площадок by LegalRC Площадки постоянно атакуют друг друга, возможны долгие подключения и лаги. Дождь из - обычная погода в моем округе. В подавали сайта есть кнопка "команд сайта" там все модераторы. Ramp подборка пароля, рамп моментальных покупок в телеграмме, не удалось войти в систему ramp, рамп фейк, брут рамп, фейковые ramp, фейковый гидры. Альтернативные даркнет площадки типа Гидры.!! Гидра не работает почему - Немецкие силовики заявили о блокировке «Гидры». Как узнать ссылку на матангу, официальная ссылка на матангу 2021, фальшивые гидры matangapchela com, сайт матанга проблемы onion top com, матанга онион не работает сайт. В 11 регионах России открыты 14 торговых центров мега. Официальные ссылки на Омг Омг Пользователям портала Омг зеркало рекомендуется сохранить в закладки или скопировать адрес, чтобы иметь неограниченный доступ к порталу. Этот сайт содержит 2 исходящих ссылок.
Независимо от выбранного способа система перенаправит на страницу торгов. Onion - Facebook, та самая социальная сеть. Как искать сайты в Даркнете? Новости ( перейти к ленте всех новостей ). Один из возможных вариантов решения проблемы. Кардинг / Хаккинг. Onion имейл. Просмотр. Vtg3zdwwe4klpx4t.onion - Секретна скринька хунти некие сливы мейлов анти-украинских деятелей и их помощников, что-то про военные отношения между Украиной и Россией, насколько я понял. Обязательно сохраните бэкапы Двухфакторная аутентификация на вход теперь активирована. Фарту масти АУЕ! Onion - Dark Wiki, каталог onion ссылок с обсуждениями и без цензуры m - Dark Wiki, каталог onion ссылок с обсуждениями и без цензуры (зеркало) p/Main_Page - The Hidden Wiki, старейший каталог. Без перерыва на обед и в туалет сходить. Суббота/Воскресенье - выходной. Pastebin / Записки. Сети децентрализованы, поэтому не контролируются кем-то одним. Официальные зеркала kraken Площадка постоянно подвергается атаке, возможны долгие подключения и лаги. Читайте полную статью: Верификация на бирже что нужно знать о KYC и AML Трейдинг на бирже Kraken Для того, чтобы начать торговлю на Kraken, необходимо: Перейти на страницу торгов. Также для максимальной конфиденциальности некоторые пользователи используют биткоин-миксеры. К. Маржинальная торговля Маржинальная торговля позволяет трейдеру открывать позиции на средства, превышающие баланс его счета. Зарубежный форум соответствующей тематики. Действительно безобидный софт в даркнете обычно не заказывают. Запустить программу и подождать, пока настроится соединение. Сохраните предложенный файл, нажав на Download. Иран. Это вкусные, аппетитные и низкокалорийные моллюски, которые удобно использовать для запекания и украшения стола. Та же ситуация касается и даркнет-маркетов. Если вход будет произведен с мобильного - в AppStore и Google Play есть специальное приложение, которое нужно скачать и установить на ваше устройство. Мы считаем, что лучше зарабатывать на расширении аудитории покупателей и предоставлении лучших предложений, а не на том, чтобы продавать дешевый хлам за высокий ценник! Whisper4ljgxh43p.onion - Whispernote Одноразовые записки с шифрованием, есть возможность прицепить картинки, ставить пароль и количество вскрытий записки. И в случае возникновения проблем, покупатель сможет открыть диспут по своему заказу, в который он также может пригласить модератора. Самым ярким примером даркнет маркета была hydra. I2P это анонимная сеть, которая представляет собой альтернативу Tor. Onion - Бразильчан Зеркало сайта brchan. Если криптовалюты у вас нет, воспользуйтесь обменниками, которые работают на площадке и помогут с пополнением счета.